The transformer must be protected against possible overcurrents or short circuits that may occur in the electrical grid, thus guaranteeing the correct operation of the installation, avoiding failures and their destruction.
The effectiveness of protections in transformers is essential to minimize the damage caused by faults of the transformer itself, and to avoid short circuits and overloads of external origin.
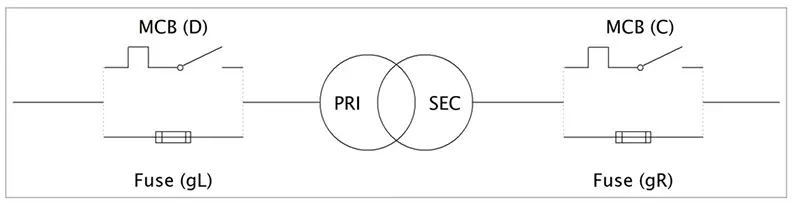
Primary -> Against short circuits: The protections must be dimensioned according to the inrush current
Secondary -> Against overloads: The protections are dimensioned at the nominal current (In) as maximum
| Inrush current | PRIMARY | SECONDARY |
|---|---|---|
| <=12In | 1.5÷2xIn curve D or fuse gL | In curve C or fast fuse gR |
| <=8In | In curve D or fuse gL | In curve C or fast fuse gR |
| <=5In | In curve C or fuse gL | In curve C or fast fuse gR |
*In = Rated current (A)
The nominal value must be less than or equal to that obtained from the calculation of the nominal current of the transformer
SINGLE-PHASE: In = Nominal power / Nominal voltage
THREE-PHASE: In= Nominal power / ( √3 *Nominal voltage)
All transformers manufactured by POLYLUX have an inrush current <=12In since high quality magnetic cores are used and the degree of compaction is high.
The standardized 8In products are:
Clinical use transformers | TH, THX, TTH, TTHX, TTHW
Ecological transformers | TTGZ, TTGW, TTDZ
At POLYLUX we have developed a tool that allows you to calculate the recommended protections for single-phase transformers and for three-phase transformers and autotransformers.
Discover the tool here
Share this tutorial
Related tutoriales
Newsletter
RECEIVE OUR NEWS IN YOUR E-MAIL